Thioredoxin and TRAF family proteins regulate reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of ASK1 through reciprocal modulation of the N-terminal homophilic interaction of ASK1
- PMID: 17724081
- PMCID: PMC2169188
- DOI: V体育ios版 - 10.1128/MCB.00227-07
Thioredoxin and TRAF family proteins regulate reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of ASK1 through reciprocal modulation of the N-terminal homophilic interaction of ASK1
Abstract
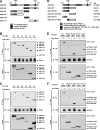
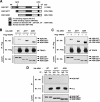
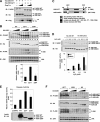
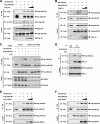
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase family, plays pivotal roles in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced cellular responses. In resting cells, endogenous ASK1 constitutively forms a homo-oligomerized but still inactive high-molecular-mass complex including thioredoxin (Trx), which we designated the ASK1 signalosome. Upon ROS stimulation, the ASK1 signalosome unbinds from Trx and forms a fully activated higher-molecular-mass complex, in part by recruitment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and TRAF6. However, the precise mechanisms by which Trx inhibits and TRAF2 and TRAF6 activate ASK1 have not been elucidated fully. Here we demonstrate that the N-terminal homophilic interaction of ASK1 through the N-terminal coiled-coil domain is required for ROS-dependent activation of ASK1. Trx inhibited this interaction of ASK1, which was, however, enhanced by expression of TRAF2 or TRAF6 or by treatment of cells with H2O2. Furthermore, the H2O2-induced interaction was reduced by double knockdown of TRAF2 and TRAF6. These findings demonstrate that Trx, TRAF2, and TRAF6 regulate ASK1 activity by modulating N-terminal homophilic interaction of ASK1 VSports手机版. .
Figures


References
-
- Chen, J., K. Fujii, L. Zhang, T. Roberts, and H. Fu. 2001. Raf-1 promotes cell survival by antagonizing apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 through a MEK-ERK independent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:7783-7788. - VSports - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujino, G., T. Noguchi, K. Takeda, and H. Ichijo. 2006. Thioredoxin and protein kinases in redox signaling. Semin. Cancer Biol. 16:427-435. - PubMed
-
- Galvan, V., A. Logvinova, S. Sperandio, H. Ichijo, and D. E. Bredesen. 2003. Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) signaling inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1). J. Biol. Chem. 278:13325-13332. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto, Y., T. Niikura, T. Chiba, E. Tsukamoto, H. Kadowaki, H. Nishitoh, Y. Yamagishi, M. Ishizaka, M. Yamada, M. Nawa, K. Terashita, S. Aiso, H. Ichijo, and I. Nishimoto. 2003. The cytoplasmic domain of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta protein precursor causes sustained apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated neurotoxic signal via dimerization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 306:889-902. - PubMed
-
- Hatai, T., A. Matsuzawa, S. Inoshita, Y. Mochida, T. Kuroda, K. Sakamaki, K. Kuida, S. Yonehara, H. Ichijo, and K. Takeda. 2000. Execution of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-induced apoptosis by the mitochondria-dependent caspase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:26576-26581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous (V体育2025版)
