Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development (VSports在线直播)
- PMID: 17325210
- PMCID: "V体育2025版" PMC2064027
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200610046
"VSports注册入口" Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
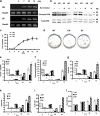
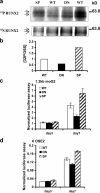
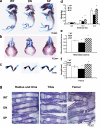
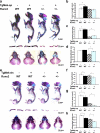
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway provides a major link between the cell surface and nucleus to control proliferation and differentiation. However, its in vivo role in skeletal development is unknown. A transgenic approach was used to establish a role for this pathway in bone. MAPK stimulation achieved by selective expression of constitutively active MAPK/ERK1 (MEK-SP) in osteoblasts accelerated in vitro differentiation of calvarial cells, as well as in vivo bone development, whereas dominant-negative MEK1 was inhibitory VSports手机版. The involvement of the RUNX2 transcription factor in this response was established in two ways: (a) RUNX2 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity were elevated in calvarial osteoblasts from TgMek-sp mice and reduced in cells from TgMek-dn mice, and (b) crossing TgMek-sp mice with Runx2+/- animals partially rescued the hypomorphic clavicles and undemineralized calvaria associated with Runx2 haploinsufficiency, whereas TgMek-dn; Runx2+/- mice had a more severe skeletal phenotype. This work establishes an important in vivo function for the ERK-MAPK pathway in bone that involves stimulation of RUNX2 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. .
Figures

References
-
- Adams, M., M.J. Reginato, D. Shao, M.A. Lazar, and V.K. Chatterjee. 1997. Transcriptional activation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is inhibited by phosphorylation at a consensus mitogen-activated protein kinase site. J. Biol. Chem. 272:5128–5132. - PubMed
-
- Celil, A.B., and P.G. Campbell. 2005. BMP-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I mediate Osterix (Osx) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells via the MAPK and protein kinase D signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 280:31353–31359. - PubMed
-
- Celil, A.B., J.O. Hollinger, and P.G. Campbell. 2005. Osx transcriptional regulation is mediated by additional pathways to BMP2/Smad signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 95:518–528. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C., A.J. Koh, N.S. Datta, J. Zhang, E.T. Keller, G. Xiao, R.T. Franceschi, N.J. D'Silva, and L.K. McCauley. 2004. Impact of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway on parathyroid hormone-related protein actions in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 279:29121–29129. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Ducy, P., and G. Karsenty. 1995. Two distinct osteoblast-specific cis-acting elements control expression of a mouse osteocalcin gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:1858–1869. - "VSports手机版" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports app下载 - Actions
VSports在线直播 - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports" Actions
"VSports手机版" Substances
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

