"V体育平台登录" Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates neuropathology in congenital inferior division oculomotor palsy
- PMID: 17070486
- PMCID: PMC1865109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2006.04.007
Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates neuropathology in congenital inferior division oculomotor palsy
Abstract
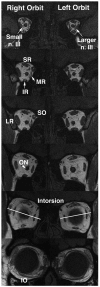
Isolated inferior division oculomotor nerve palsy (ONP) is rare VSports手机版. Acquired cases have been associated with neurologic or systemic disease. To our knowledge, congenital inferior division ONP is previously unreported. We present a case of congenital inferior division ONP in which magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated the structural neuropathy. .
Figures


References
-
- Karim S, Clark RA, Poukens V, Demer JL. Demonstration of systematic variation in human intraorbital optic nerve size by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:1047–51. - PubMed
-
- Good WV, Barkovich AJ, Nickel BL, Hoyt CS. Bilateral congenital oculomotor nerve palsy in a child with brain anomalies. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991;111:555–8. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Nagata E, Tanahashi N, Koto A, Fukuuchi Y, Kayama H. A case of spontaneous arteriovenous fistula presenting as the partial oculomotor nerve palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1995;35:808–10. - PubMed
-
- Takano M, Aoki K. Midbrain infarction presenting isolated inferior rectus nuclear palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaka. 2000;40:832–5. - PubMed
-
- Chou TM, Demer JL. Isolated inferior rectus palsy caused by a metastasis to the oculomotor nucleus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998;126:737–40. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
"VSports最新版本" MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
VSports在线直播 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports app下载 - Medical

