Loss of hepatic NF-kappa B activity enhances chemical hepatocarcinogenesis through sustained c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation
- PMID: 16807293
- PMCID: PMC1502270
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603499103
"V体育官网" Loss of hepatic NF-kappa B activity enhances chemical hepatocarcinogenesis through sustained c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation
Abstract
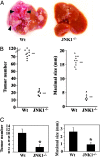
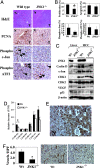
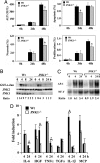
A major link between inflammation and cancer is provided by NF-kappaB transcription factors. Ikkbeta(Deltahep) mice, which specifically lack IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta), an activator of NF-kappaB, in hepatocytes, are unable to activate NF-kappaB in response to proinflammatory stimuli, such as TNF-alpha. Surprisingly, Ikkbeta(Deltahep) mice are hypersusceptible to diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Because defective NF-kappaB activation promotes sustained c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation in cells exposed to TNF-alpha, whose expression is induced by DEN, and JNK activity is required for normal hepatocyte proliferation, we examined whether increased susceptibility to DEN-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in Ikkbeta(Deltahep) mice requires JNK activation. Hepatocytes express both JNK1 and JNK2, but previous studies indicate that JNK1 is more important for hepatocyte proliferation. We therefore investigated this hypothesis using mice homozygous for a JNK1 deficiency either in wild-type or Ikkbeta(Deltahep) backgrounds. In both cases, mice lacking JNK1 were much less susceptible to DEN-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. This impaired tumorigenesis correlated with decreased expression of cyclin D and vascular endothelial growth factor, diminished cell proliferation, and reduced tumor neovascularization. Whereas hepatocyte-specific deletion of IKKbeta augmented DEN-induced hepatocyte death and cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation, disruption of JNK1 abrogated this response. In addition to underscoring the importance of JNK1-mediated hepatocyte death and compensatory proliferation, these results strongly suggest that the control of tissue renewal through the IKK and JNK pathways plays a key role in liver carcinogenesis. VSports手机版.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
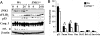
References
-
- Thorgeirsson S. S., Grisham J. W. Nat. Genet. 2002;31:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Bosch F. X., Ribes J., Diaz M., Cleries R. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5–S16. - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
-
- Maeda S., Kamata H., Luo J. L., Leffert H., Karin M. Cell. 2005;121:977–990. - PubMed
-
- Fausto N. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999;19:243–252. - PubMed
V体育安卓版 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
"VSports" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials (VSports注册入口)
Miscellaneous (V体育官网)

