VSports注册入口 - Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy
- PMID: 16520392
- PMCID: PMC2118227
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20052283
"VSports注册入口" Antibody isotype-specific engagement of Fcgamma receptors regulates B lymphocyte depletion during CD20 immunotherapy
Abstract
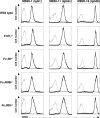
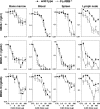
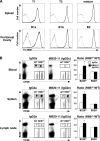
CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) immunotherapy is effective for lymphoma and autoimmune disease. In a mouse model of immunotherapy using mouse anti-mouse CD20 mAbs, the innate monocyte network depletes B cells through immunoglobulin (Ig)G Fc receptor (FcgammaR)-dependent pathways with a hierarchy of IgG2a/c>IgG1/IgG2b>IgG3. To understand the molecular basis for these CD20 mAb subclass differences, B cell depletion was assessed in mice deficient or blocked for stimulatory FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, FcgammaRIV, or FcR common gamma chain, or inhibitory FcgammaRIIB. IgG1 CD20 mAbs induced B cell depletion through preferential, if not exclusive, interactions with low-affinity FcgammaRIII. IgG2b CD20 mAbs interacted preferentially with intermediate affinity FcgammaRIV. The potency of IgG2a/c CD20 mAbs resulted from FcgammaRIV interactions, with potential contributions from high-affinity FcgammaRI. Regardless, FcgammaRIV could mediate IgG2a/b/c CD20 mAb-induced depletion in the absence of FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIII. In contrast, inhibitory FcgammaRIIB deficiency significantly increased CD20 mAb-induced B cell depletion by enhancing monocyte function VSports手机版. Although FcgammaR-dependent pathways regulated B cell depletion from lymphoid tissues, both FcgammaR-dependent and -independent pathways contributed to mature bone marrow and circulating B cell clearance by CD20 mAbs. Thus, isotype-specific mAb interactions with distinct FcgammaRs contribute significantly to the effectiveness of CD20 mAbs in vivo, which may have important clinical implications for CD20 and other mAb-based therapies. .
VSports - Figures

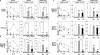
References
-
- Takai, T. 2002. Roles of Fc receptors in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:580–592. - VSports注册入口 - PubMed
-
- Ravetch, J.V. 2003. Fc receptors. In Fundamental Immunology. W.E. Paul, editor. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, PA. 685–700.
-
- Davis, R.S., G. Dennis Jr., M.R. Odom, A.W. Gibson, R.P. Kimberly, P.D. Burrows, and M.D. Cooper. 2002. Fc receptor homologs: newest members of a remarkably diverse Fc receptor gene family. Immunol. Rev. 190:123–136. - PubMed
-
- Mechetina, L.V., A.M. Najakshin, B.Y. Alabyev, N.A. Chikaev, and A.V. Taranin. 2002. Identification of CD16-2, a novel mouse receptor homologous to CD16/FcγRIII. Immunogenetics. 54:463–468. - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn, F., P. Bruhns, K. Horiuchi, and J.V. Ravetch. 2005. FcγRIV: a novel FcR with distinct IgG subclass specificity. Immunity. 23:41–51. - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
Substances (VSports手机版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Grants and funding
"VSports" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"VSports在线直播" Molecular Biology Databases

