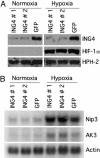
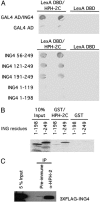
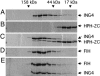
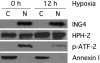
The candidate tumor suppressor ING4 represses activation of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)
- PMID: 15897452
- PMCID: PMC1140452
- DOI: "V体育安卓版" 10.1073/pnas.0502716102
The candidate tumor suppressor ING4 represses activation of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)
Abstract
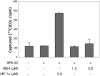
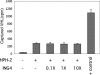
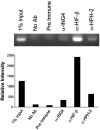
The hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) plays an important role in the progression of a number of pathophysiological processes including tumorigenesis. In addition to several well characterized oxygen-dependent modes of regulation, the function of the HIF transcription factor can also be influenced through the action of other regulatory pathways. Misregulation of these factors resulting in inappropriate HIF expression or activity can contribute to the progression of human cancers through the induction of genes promoting angiogenesis, glycolysis, cell survival, and metastasis, among other processes. The candidate tumor suppressor protein inhibitor of growth family member 4 (ING4) has recently been implicated as a repressor of angiogenesis and tumor growth through association with NF-kappaB. Here we demonstrate that suppression of ING4 further induces HIF transcriptional activity as well. ING4 directly associates with the HIF prolyl hydroxylase, an Fe(II)-dependent oxygenase previously shown to mediate HIF stability as a function of oxygen availability. However, rather than affecting HIF's stability, ING4 mediates HIF's activity. These data support a model in which, in addition to regulating HIF stability, HIF prolyl hydroxylases can modulate HIF function through the recruitment of ING4, a likely component of a chromatin-remodeling complex VSports手机版. .
V体育2025版 - Figures

References
-
- Wenger, R. H. (2002) FASEB J. 16, 1151–1162. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Maxwell, P. H. & Ratcliffe, P. J. (2002) Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 29–37. - PubMed
-
- Bruick, R. K. (2003) Genes Dev. 17, 2614–2623. - PubMed
-
- Epstein, A. C. R., Gleadle, J. M., McNeil, L. A., Hewitson, K. S., O'Rourke, J., Mole, D. R., Mukherji, M., Metzen, E., Wilson, M. I., Dhanda, A., et al. (2001) Cell 107, 43–54. - PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"VSports" MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
VSports注册入口 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育官网入口)
Molecular Biology Databases

