Estradiol and selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate target genes with estrogen receptors alpha and beta
- PMID: 14699072
- PMCID: PMC363122
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-06-0360 (VSports在线直播)
"VSports手机版" Estradiol and selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate target genes with estrogen receptors alpha and beta
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
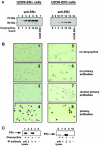
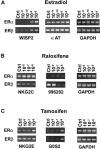
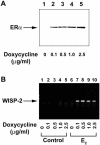
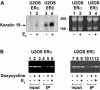
Estrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) interact with estrogen receptor (ER) alpha and beta to activate or repress gene transcription. To understand how estrogens and SERMs exert tissue-specific effects, we performed microarray analysis to determine whether ERalpha or ERbeta regulate different target genes in response to estrogens and SERMs. We prepared human U2OS osteosarcoma cells that are stably transfected with a tetracycline-inducible vector to express ERalpha or ERbeta. Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation studies confirmed that U2OS-ERalpha cells synthesized only ERalpha and that U2OS-ERbeta cells expressed exclusively ERbeta. U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells were treated either with 17beta-estradiol (E2), raloxifene, and tamoxifen for 18 h. Labeled cRNAs were hybridized with U95Av2 GeneChips (Affymetrix). A total of 228, 190, and 236 genes were significantly activated or repressed at least 1. 74-fold in U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells by E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen, respectively. Most genes regulated in ERalpha cells in response to E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen were distinct from those regulated in ERbeta cells. Only 38 of the 228 (17%) genes were regulated by E2 in both U2OS-ERalpha and U2OS-ERbeta cells VSports手机版. Raloxifene and tamoxifen regulated only 27% of the same genes in both the ERalpha and ERbeta cells. A subset of genes involved in bone-related activities regulated by E2, raloxifene, and tamoxifen were also distinct. Our results demonstrate that most genes regulated by ERalpha are distinct from those regulated by ERbeta in response to E2 and SERMs. These results indicate that estrogens and SERMs exert tissue-specific effects by regulating unique sets of targets genes through ERalpha and ERbeta .
Figures


V体育官网 - References
-
- Abdelrahim, M., Samudio, I., Smith, R., 3rd, Burghardt, R., and Safe, S. (2002). Small inhibitory RNA duplexes for Sp1 mRNA block basal and estrogen-induced gene expression and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28815-28822. - PubMed
-
- An, J., Ribeiro, R.C., Webb, P., Gustafsson, J.A., Kushner, P.J., Baxter, J.D., and Leitman, D.C. (1999). Estradiol repression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha transcription requires estrogen receptor activation function-2 and is enhanced by coactivators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15161-15166. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- An, J., Tzagarakis-Foster, C., Scharschmidt, T.C., Lomri, N., and Leitman, D.C. (2001). Estrogen receptor beta-selective transcriptional activity and recruitment of coregulators by phytoestrogens. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17808-17814. - PubMed
-
- Anzick, S.L., Kononen, J., Walker, R.L., Azorsa, D.O., Tanner, M.M., Guan, X.Y., Sauter, G., Kallioniemi, O.P., Trent, J.M., and Meltzer, P.S. (1997). AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277, 965-968. - PubMed
-
- Baker, V., Draper, M., Paul, S., Allerheiligen, S., Glant, M., Shirfren, J., and Jaffe, R. (1998). Reproductive endocrine and endometrial effects of raloxifene hydrochloride, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, in women with regular menstrual cycles. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 6-13. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
VSports手机版 - Publication types
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
V体育官网入口 - MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网)
"VSports在线直播" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
V体育官网入口 - Other Literature Sources
Research Materials (V体育安卓版)

