Skeletal malformations caused by overexpression of Cbfa1 or its dominant negative form in chondrocytes
- PMID: 11285276
- PMCID: PMC2185519
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.1.87 (V体育官网入口)
Skeletal malformations caused by overexpression of Cbfa1 or its dominant negative form in chondrocytes (VSports注册入口)
V体育ios版 - Abstract
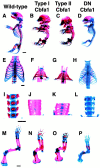
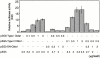
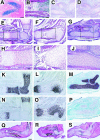
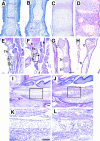
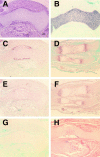
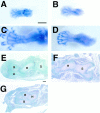
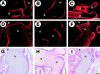
During skeletogenesis, cartilage develops to either permanent cartilage that persists through life or transient cartilage that is eventually replaced by bone. However, the mechanism by which cartilage phenotype is specified remains unclarified. Core binding factor alpha1 (Cbfa1) is an essential transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation and has the ability to stimulate chondrocyte maturation in vitro. To understand the roles of Cbfa1 in chondrocytes during skeletal development, we generated transgenic mice that overexpress Cbfa1 or a dominant negative (DN)-Cbfa1 in chondrocytes under the control of a type II collagen promoter/enhancer. Both types of transgenic mice displayed dwarfism and skeletal malformations, which, however, resulted from opposite cellular phenotypes VSports手机版. Cbfa1 overexpression caused acceleration of endochondral ossification due to precocious chondrocyte maturation, whereas overexpression of DN-Cbfa1 suppressed maturation and delayed endochondral ossification. In addition, Cbfa1 transgenic mice failed to form most of their joints and permanent cartilage entered the endochondral pathway, whereas most chondrocytes in DN-Cbfa1 transgenic mice retained a marker for permanent cartilage. These data show that temporally and spatially regulated expression of Cbfa1 in chondrocytes is required for skeletogenesis, including formation of joints, permanent cartilages, and endochondral bones. .
Figures

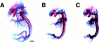

References
-
- Chung K.S., Park H.H., Ting K., Takita H., Apte S.S., Kuboki Y., Nishimura I. Modulated expression of type X collagen in Meckel's cartilage with different developmental fates. Dev. Biol. 1995;170:387–396. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Ducy P., Zhang R., Geoffroy V., Ridall A.L., Karsenty G. Osf2/Cbfa1a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell. 1997;89:747–754. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Ducy P., Starbuck M., Priemel M., Shen J., Pinero G., Geoffroy V., Amling M., Karsenty G. A Cbfa1-dependent genetic pathway controls bone formation beyond embryonic development. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1025–1036. - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Enomoto H., Enomoto-Iwamoto M., Iwamoto M., Nomura S., Himeno M., Kitamura Y., Kishimoto T., Komori T. Cbfa1 is a positive regulatory factor in chondrocyte maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:8695–8702. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto-Iwamoto M., Iwamoto M., Mukudai Y., Kawakami Y., Nohno T., Higuchi Y., Takemoto S., Ohuchi H., Noji S., Kurisu K. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling is required for maintenance of differentiated phenotype, control of proliferation, and hypertrophy in chondrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1998;140:409–418. - PMC - PubMed
"V体育平台登录" Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

