Chromosome instability and defective recombinational repair in knockout mutants of the five Rad51 paralogs
- PMID: 11283264
- PMCID: PMC86915
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2858-2866.2001
VSports注册入口 - Chromosome instability and defective recombinational repair in knockout mutants of the five Rad51 paralogs
Abstract
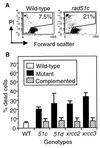
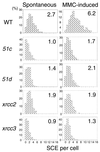
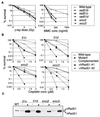
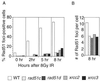
The Rad51 protein, a eukaryotic homologue of Escherichia coli RecA, plays a central role in both mitotic and meiotic homologous DNA recombination (HR) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is essential for the proliferation of vertebrate cells. Five vertebrate genes, RAD51B, -C, and -D and XRCC2 and -3, are implicated in HR on the basis of their sequence similarity to Rad51 (Rad51 paralogs). We generated mutants deficient in each of these proteins in the chicken B-lymphocyte DT40 cell line and report here the comparison of four new mutants and their complemented derivatives with our previously reported rad51b mutant. The Rad51 paralog mutations all impair HR, as measured by targeted integration and sister chromatid exchange. Remarkably, the mutant cell lines all exhibit very similar phenotypes: spontaneous chromosomal aberrations, high sensitivity to killing by cross-linking agents (mitomycin C and cisplatin), mild sensitivity to gamma rays, and significantly attenuated Rad51 focus formation during recombinational repair after exposure to gamma rays VSports手机版. Moreover, all mutants show partial correction of resistance to DNA damage by overexpression of human Rad51. We conclude that the Rad51 paralogs participate in repair as a functional unit that facilitates the action of Rad51 in HR. .
Figures

"VSports最新版本" References
-
- Albala J S, Thelen M P, Prange C, Fan W, Christensen M, Thompson L H, Lennon G G. Identification of a novel human RAD51 homolog, RAD51B. Genomics. 1997;46:476–479. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, West S C. Role of the human RAD51 protein in homologous recombination and double-stranded-break repair. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:247–251. - PubMed
-
- Bennett R J, Dunderdale H J, West S C. Resolution of Holliday junctions by RuvC resolvase: cleavage specificity and DNA distortion. Cell. 1993;74:1021–1031. - PubMed (VSports在线直播)
-
- Bezzubova O Y, Silbergleit A, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Takeda S, Buerstedde J M. Reduced X-ray resistance and homologous recombination frequencies in a RAD54-/- mutant of the chicken DT40 cell line. Cell. 1997;89:185–193. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Bianco P R, Tracy R B, Kowalczykowski S C. DNA strand exchange proteins: a biochemical and physical comparison. Front Biosci. 1998;3:D570–D603. - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
"V体育安卓版" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
