CMS: an adapter molecule involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements
- PMID: 10339567
- PMCID: PMC26861
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6211
CMS: an adapter molecule involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements
Abstract
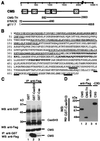
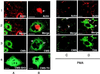
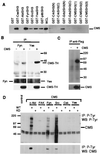
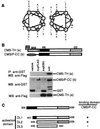
Cas ligand with multiple Src homology (SH) 3 domains (CMS) is an ubiquitously expressed signal transduction molecule that interacts with the focal adhesion protein p130(Cas). CMS contains three SH3 in its NH2 terminus and proline-rich sequences in its center region. The latter sequences mediate the binding to the SH3 domains of p130(Cas), Src-family kinases, p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Grb2. The COOH-terminal region contains putative actin binding sites and a coiled-coil domain that mediates homodimerization of CMS. CMS is a cytoplasmic protein that colocalizes with F-actin and p130(Cas) to membrane ruffles and leading edges of cells. Ectopic expression of CMS in COS-7 cells resulted in alteration in arrangement of the actin cytoskeleton. We observed a diffuse distribution of actin in small dots and less actin fiber formation. Altogether, these features suggest that CMS functions as a scaffolding molecule with a specialized role in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. VSports手机版.
Figures

References
-
- Keely P, Parise L, Juliano R. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:101–106. - PubMed
-
- Clezardin P. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998;54:541–548. - VSports在线直播 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clark E A, Brugge J S. Science. 1995;268:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Howe A, Aplin A E, Alahari S K, Juliano R L. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:220–231. - PubMed
-
- Ojaniemi M, Vuori K. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25993–25998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - Actions
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Associated data (VSports在线直播)
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
"VSports最新版本" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

